Railway Power Analysis & Power System Testing
High-speed and high-channel-count data acquisition solutions for railway testing applications like pantograph and conductor rail testing, short circuit analysis and power system testing.
High-speed and high-channel-count data acquisition solutions for railway testing applications like pantograph and conductor rail testing, short circuit analysis and power system testing.
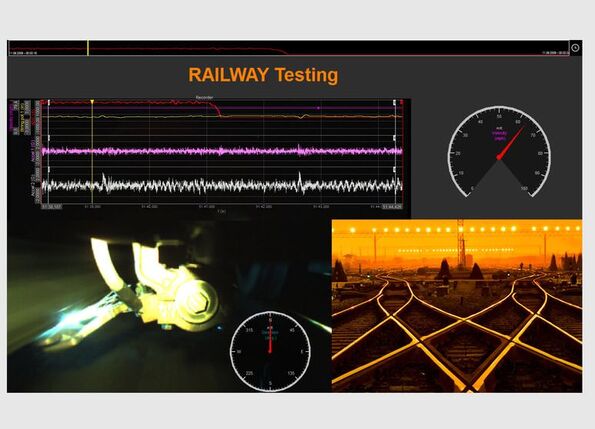
Pantograph & Conductor Rail Testing
Train and railways are operated with either DC and AC power. They are operated at different voltage levels (250 V to 66 kV) and different line frequencies (16.7 Hz, 25 Hz, 50 Hz, 60 Hz). The trains get the power whether via a pantograph which is connected to overhead lines or via a conductor rail (3rd rail).
Testing the power supply system requires a high precision DAQ system that supports a wide range of input signals like voltage, current, acceleration, GPS parameters, CAN-bus data, video and displacement. Especially synchronized video is very important and useful for comprehensive analysis (monitoring connection of pantograph to overhead line, interaction of rails and conductor rail etc.) In addition to the high voltages also the high operating currents up to 8000A are present which require special current transducers (AC and DC).
Train and railways are operated with either DC and AC power. They are operated at different voltage levels (250 V to 66 kV) and different line frequencies (16.7 Hz, 25 Hz, 50 Hz, 60 Hz). The trains get the power whether via a pantograph which is connected to overhead lines or via a conductor rail (3rd rail).
Testing the power supply system requires a high precision DAQ system that supports a wide range of input signals like voltage, current, acceleration, GPS parameters, CAN-bus data, video and displacement. Especially synchronized video is very important and useful for comprehensive analysis (monitoring connection of pantograph to overhead line, interaction of rails and conductor rail etc.) In addition to the high voltages also the high operating currents up to 8000A are present which require special current transducers (AC and DC).
Short Circuit Analysis
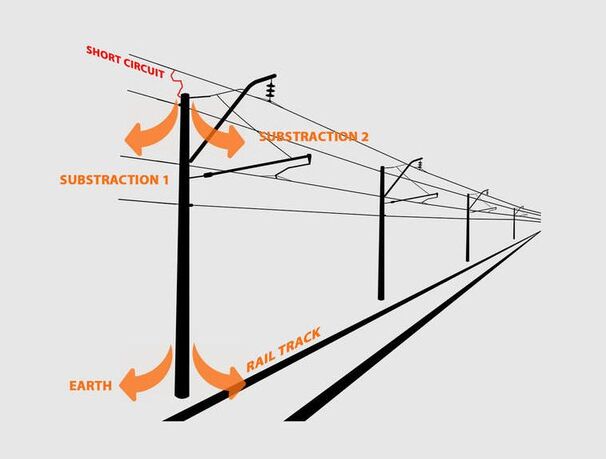
Short-circuit analysis at railway power supply system is a typical application for the Transient recording function of the Dewesoft Power Analyzer. At the expansion of short-circuits in railway power supply systems it is often assumed that the short-circuit current is split into thirds. 1/3 flows via the return conductor, 1/3 via the rail track and 1/3 into the earth. In reality, the results differ a lot and strongly depends on the ambient conditions (grounding, soil, etc).
Dewesoft power analyzer allows measuring the expansion of the short-circuit with automatic evaluation. Parameters like peak current, AC and DC part of the short circuit, time of the short circuit and a lot more can be calculated. Furthermore, high-speed cameras and thermal imaging cameras can be connected to the system and acquired synchronously for comprehensive analysis.
Short-circuit analysis at railway power supply system is a typical application for the Transient recording function of the Dewesoft Power Analyzer. At the expansion of short-circuits in railway power supply systems it is often assumed that the short-circuit current is split into thirds. 1/3 flows via the return conductor, 1/3 via the rail track and 1/3 into the earth. In reality, the results differ a lot and strongly depends on the ambient conditions (grounding, soil, etc).
Dewesoft power analyzer allows measuring the expansion of the short-circuit with automatic evaluation. Parameters like peak current, AC and DC part of the short circuit, time of the short circuit and a lot more can be calculated. Furthermore, high-speed cameras and thermal imaging cameras can be connected to the system and acquired synchronously for comprehensive analysis.
Power System Testing
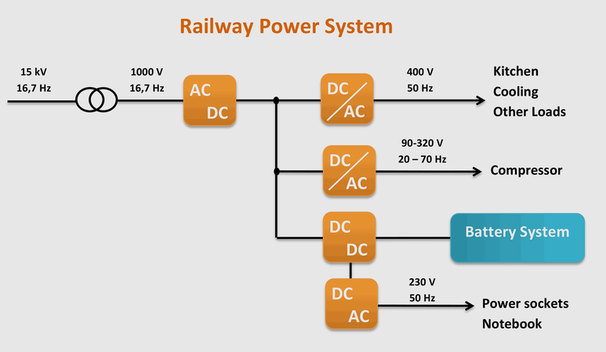
The electrical power for the train systems is either provided by a third rail or an overhead line via a pantograph. Inside the rail, the power has to be transformed to allow the operation of the different equipment. Typically, a train at first transforms the high supply voltage (e.g. 15 kV) down to a lower voltage range (< 1000 V). The power is then further transformed to different voltage levels and inverted to different frequencies (e.g. 16.7 Hz, 50 Hz, 25 Hz, DC).
The electrical power for the train systems is either provided by a third rail or an overhead line via a pantograph. Inside the rail, the power has to be transformed to allow the operation of the different equipment. Typically, a train at first transforms the high supply voltage (e.g. 15 kV) down to a lower voltage range (< 1000 V). The power is then further transformed to different voltage levels and inverted to different frequencies (e.g. 16.7 Hz, 50 Hz, 25 Hz, DC).
|
Typical Configuration
Short Circuit Analysis For the typical configuration we recommend R2DB DAQ system configured for: 1 x Voltage 7 x Current Highlights High sampling rate Raw data storing Triggering on different channels (analog, digital, math, power, power quality, etc.) Analysis at all line frequencies (16.7 Hz, 50 Hz, 60 Hz, etc.) |